What is Biaxial Geogrid?
Biaxial geogrid is a material widely used in civil engineering and infrastructure construction, mainly used to enhance the strength and stability of soil. This material plays an important role in roadbed construction, embankment reinforcement, slope stabilization, etc. with its unique structure and versatility.
What is biaxial geogrid?
Definition and construction of biaxial geogrid:
Biaxial geogrid is a mesh structure made of high molecular polymer material. The "biaxial" in its name refers to the fact that it has the same tensile strength in two orthogonal directions. This grid is usually manufactured through an extrusion and stretching process to form a regular mesh structure. The size and shape of the grid can be adjusted according to application requirements to suit different engineering projects.
The structural characteristics of biaxial geogrid enable it to evenly disperse stress in two directions, providing greater stability and support. Unlike unidirectional geogrids, biaxial geogrids are able to function simultaneously in two main directions within the horizontal plane, so it is an ideal choice in projects that require all-round support and reinforcement.
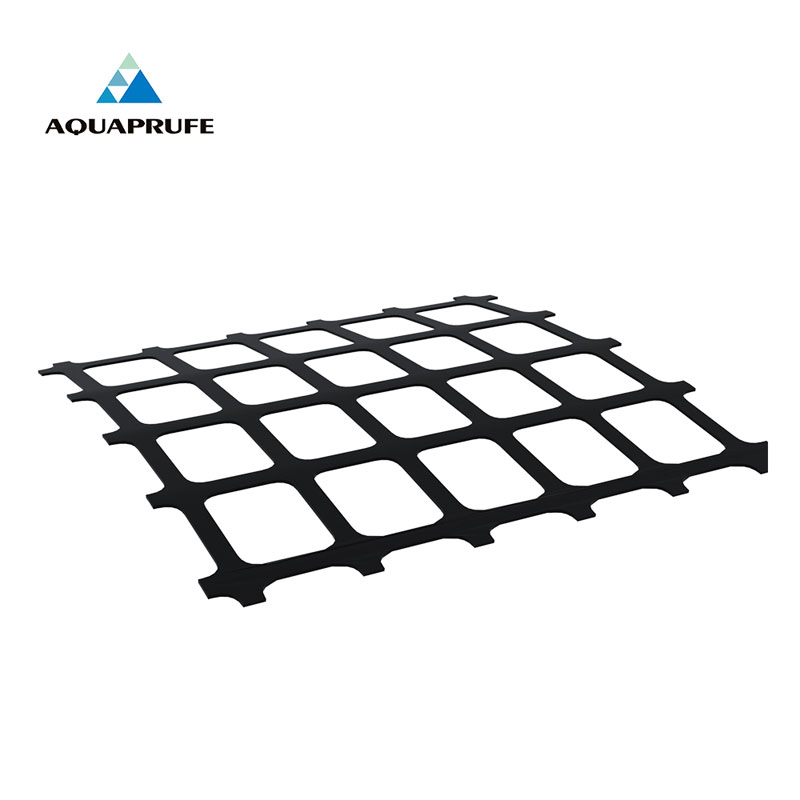
What is the purpose of using biaxial geogrid?
The main purpose of using bidirectional geogrids is to improve the overall quality and durability of the project by enhancing the structural strength and stability of the soil. Its main functions include:
● Soil reinforcement: By fixing soil particles in the grid, bidirectional geogrids can effectively prevent soil sliding and deformation, thereby enhancing the overall strength of the soil.
● Load dispersion: Bidirectional geogrids can disperse concentrated loads over a larger area, reduce local pressure, and prevent foundation sinking or deformation.
● Impact resistance: When subjected to dynamic loads such as traffic flow, bidirectional geogrids can absorb and disperse impact forces, reducing damage to the foundation and pavement.
● Reduce foundation settlement: By enhancing the bearing capacity of the foundation, bidirectional geogrids can reduce the settlement problem of the foundation and ensure the long-term stability of the pavement and structure.
What are the main uses of bidirectional geogrids?
Due to its unique functions and structural characteristics, bidirectional geogrids have been widely used in many fields. Here are some of the main uses:
● Road and railway construction: During the construction of roads and railways, bidirectional geogrids are often used to reinforce the roadbed. By increasing the bearing capacity of the foundation, it can prevent deformation and settlement of the road and track, and extend the service life of roads and railways.
● Embankment and revetment projects: Bidirectional geogrid plays a key role in embankment and revetment projects. It can enhance the stability of the embankment, prevent soil erosion and collapse, and thus protect the safety of coastal areas.
● Slope protection: In the stabilization project of hillsides or high and steep slopes, bidirectional geogrids prevent landslides and soil loss by enhancing the shear strength of the soil.
● Filling projects: In filling projects, bidirectional geogrids can improve the overall stability of the fill body and reduce settlement and deformation.
● Foundation reinforcement: In the reinforcement of building foundations, bidirectional geogrids can increase the bearing capacity of the foundation and ensure the stability and safety of the building structure.
What is the working principle of bidirectional geogrid?
The working principle of bidirectional geogrid is based on the unique characteristics of its structure and materials. Its grid structure can disperse stress when subjected to force, and evenly distribute the external force throughout the grid, thereby reducing local stress concentration in the soil.
When the bidirectional geogrid is laid in the soil, it forms an integral reinforcement system through interaction with soil particles. Soil particles are embedded in the mesh of the grid to form an interlocking structure, which can effectively limit the lateral displacement of the soil and increase the bearing capacity of the soil. In addition, the high tensile strength of the bidirectional geogrid can withstand large loads and prevent the soil from deforming due to external pressure.
This grid can also improve the stability of the soil by increasing its friction. The grid structure of the bidirectional geogrid makes it difficult for soil particles to slide under external forces, thereby further enhancing the shear strength and overall stability of the soil.

What are the Pros of bidirectional geogrid?
The reason why bidirectional geogrid is widely used in engineering construction is mainly due to its significant pros:
● Durability: Bidirectional geogrid is made of high molecular polymer and has excellent durability. It can resist ultraviolet rays, chemical corrosion and microbial erosion, ensuring its long-term performance under various environmental conditions.
● Convenient construction: Bidirectional geogrid is light in weight, easy to transport and install, which can greatly shorten the construction time and reduce construction costs.
● Economical: By improving the stability of foundations and structures, bidirectional geogrids can reduce maintenance and repair costs and reduce the cost of the entire project.
● Environmental protection: The materials of bidirectional geogrids are harmless to the environment and meet the high standards of environmental protection requirements of modern engineering.
Selection and application considerations of bidirectional geogrids
When selecting and applying bidirectional geogrids, engineers need to consider multiple factors to ensure their optimal performance in a specific project. For example, selecting high-quality materials is the key to ensuring the performance of bidirectional geogrids. The tensile strength, durability and corrosion resistance of the material directly affect its use effect.
At the same time, select the appropriate mesh size and tensile strength specifications according to the project requirements to meet different reinforcement needs. The correct construction method and process are crucial to the effect of bidirectional geogrids. During the construction process, it is necessary to ensure that the grid is laid flat and the tension is uniform to avoid wrinkles or damage.
In addition, consider the environmental conditions of the project location, such as climate, soil type, groundwater level, etc., to select the most suitable bidirectional geogrid material.
Conclusion
As a highly efficient geotechnical material, bidirectional geogrid plays an irreplaceable role in modern engineering construction. It can not only significantly improve the stability of soil and foundation, but also extend the service life of engineering structures and reduce maintenance costs. Through correct selection and application, bidirectional geogrids can provide reliable support and guarantee for various infrastructure construction.
Whether in road and railway construction, or in dams, revetments, slope reinforcement and other fields, bidirectional geogrids have demonstrated their powerful functions and advantages. Its wide application not only improves the quality and safety of projects, but also provides strong support for the development of modern engineering technology.




