How Does Geogrid Work?
Geogrid is a type of geosynthetic material made from polypropylene or polyethylene. It is used to enhance the stability of civil engineering projects, by spreading concentrated loads over a larger area, reducing settlement and movement. PP or PE sheets are punched with regular hole meshes and then stretched to form ribs that distribute loads. Typical applications are retaining walls, embankments, slopes, subgrades, and surfaces of roads, railways, airports, etc.
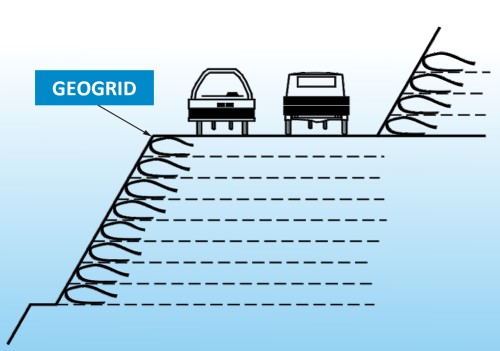
Geogrids interlock base materials within the meshes so that the stress loaded on them can be transferred into the geogrids. While the tensile resistance of geogrids is much larger than the internal friction force of base materials, geogrids can effectively hold the base materials together and prevent them from settling or moving. Hence, geogrids are ideal for stabilizing and reinforcing, especially projects with soft and weak bases.
Geogrids come in several types such as uniaxial, biaxial and triaxial. Aquaprufe provides the commonly used uniaxial and biaxial geogrids. AG-UG uniaxial geogrids, with long oval meshes, are made of punched polymer sheets stretched longitudinally. They are usually used in slopes, embankments, and retaining walls. AG-BG biaxial geogrids, with square meshes, are stretched both longitudinally and transversely. They distribute loads along both directions and are usually applied to foundations of roadbeds, railway trucks, airports, and projects on soft and weak foundations. Although these two types of geogrids seem to fit different parts in construction, they can also be used one over another to form stronger reinforcement with multiple layers of geogrids.


Aquaprufe provides overall solutions for soil reinforcement and stabilization using geosynthetics. Please feel free to contact us for more info at contact@aquaprufe.com




